 Dr. Lynn Chiam
Dr. Lynn Chiam
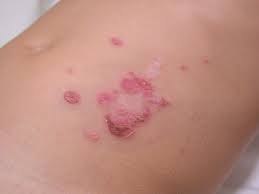
What is Impetigo?
Impetigo is a skin infection that can spread from one person to another. Impetigo causes one or more "sores" on the skin that are often covered by a thick dry honey-colored crust. The sores don't hurt, but may be tender if touched. They may also be itchy. Any skin area can be affected, but sores are usually on arms or legs, the face (mainly around the mouth, nose, or ears), and sometimes on the scalp. Anyone can get impetigo, but it most often occurs in children 2 to 6 years old. The disease is most common during summer and fall, but can occur anytime.
What Causes Impetigo?
Impetigo is usually caused by a group of bacteria ("germs") called group A streptococci ("strep"), or by other bacteria called staphylococci ("staph"). These bacteria are normally found on the skin and in the nose. When small cuts, scratches, or insect bites occur, these bacteria can get under the skin surface and cause infection. Infected areas are often reddish and puffy. Fluid or pus oozes from the sore for a few days. The fluid dries to form honey-colored crusts. As the bacteria multiply, the sores increase in number and size.
How is Impetigo Spread?
Impetigo is very contagious. Sores have large numbers of the bacteria. The bacteria are easily passed to new areas of the skin by scratching or touching the sores or to other people by unwashed hands, dirty fingernails, and clothing or other objects that have touched the sores. To help prevent spread of impetigo:
- Bathe or shower daily.
- Keep fingernails clean and short.
- Wash with hot water and soap clothing, sheets, towels, and other items that come in contact with impetigo sores or crusts. Do not share these items with anyone else.
- Keep sores covered with clean bandages. Wash your hands after changing the bandage.
- Throw away used bandages in a trash bag.
Children who may have impetigo should not attend school or daycare. They should not sleep, play, or have close contact, with other children until after they have been seen by a doctor.
Impetigo
ICD-9 684; ICD-10 L01
Texas Dept of State Health Services
 Wikipedia
WikipediaLabels: bacteria, Impetigo image, impetigo infection, insect bite, scratches, small cuts, staph, strep a
# posted by Pat O'Connor @ 9:35 AM




